As advancements in medical technology continue, diabetes treatment has entered an exciting new phase. The latest innovation in diabetes care comes from Kyoto University Hospital, where researchers are developing a technique to process pancreatic cells into sheet-like structures for transplantation under the skin. Clinical trials are expected to begin next year, bringing hope to countless individuals seeking relief from insulin injections and other conventional treatments. Let’s explore how this breakthrough, along with other emerging therapies, is transforming the outlook for diabetes patients.
The Potential of Pancreatic Cell Transplantation
Diabetes is primarily categorized into Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes, often developing in childhood, occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks pancreatic cells, rendering them incapable of producing insulin. Patients with Type 1 diabetes rely on insulin injections to regulate blood sugar. In contrast, Type 2 diabetes results from lifestyle factors such as obesity, diet, and genetics, with the pancreas still producing insulin but unable to utilize it effectively. Exercise and diet improvements can manage symptoms in some cases.
One innovative approach being explored at Kyoto University Hospital is the transplantation of processed pancreatic cells. This procedure involves creating a sheet of pancreatic cells using induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS), which are then transplanted under the skin to promote insulin production. By reintroducing functional pancreatic cells into a patient’s system, researchers hope to provide an alternative to lifelong insulin injections, enhancing quality of life and achieving a more stable blood glucose level.
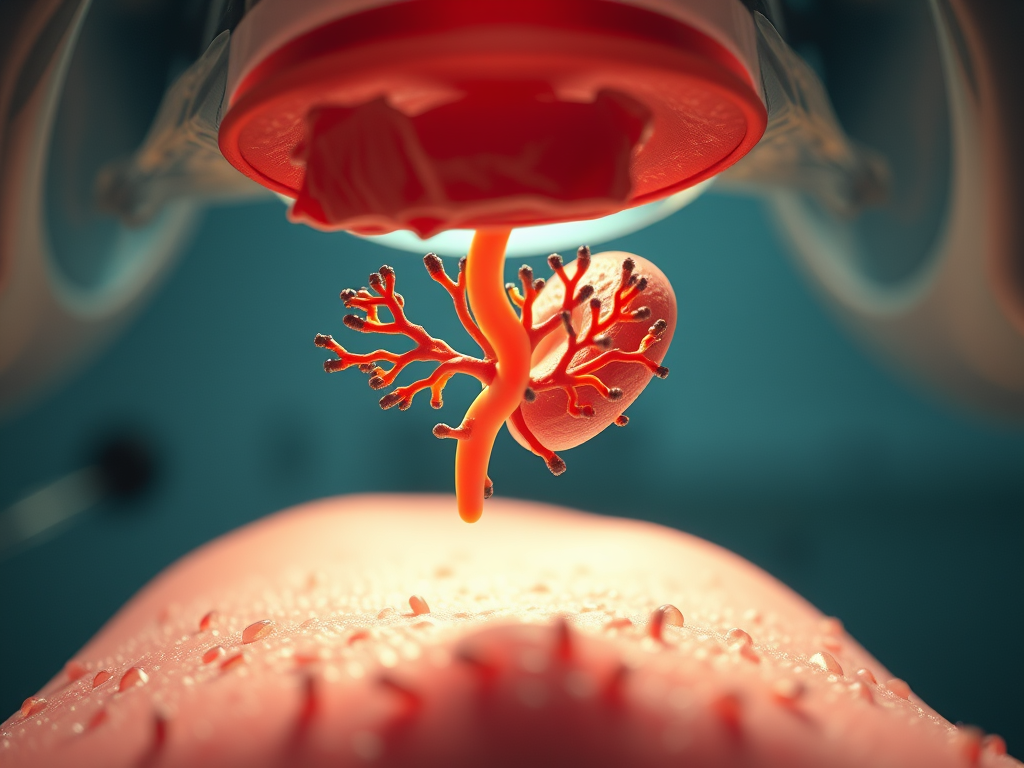
Stories of Hope: Patients’ Anticipations and Testimonials
For many diabetes patients, daily insulin injections can feel burdensome, affecting their daily lives and mental well-being. A 12-year-old patient, Emily, diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes at age 6, shares her story: “I just want to go a day without needles.” Stories like Emily’s inspire researchers to continue exploring alternatives that could allow young people with diabetes to live a life free from injections and better control their health. These personal accounts not only highlight the demand for new treatments but also reflect the genuine hope that innovations like pancreatic cell transplantation bring.
Ongoing Innovations in Type 1 Diabetes Treatment
Kyoto University Hospital’s research represents one part of a broader movement toward innovative solutions for diabetes management. Swiss biotechnology firm CRISPR Therapeutics is utilizing gene-editing technology to develop therapies that may help Type 1 patients produce insulin without external injections. This approach, while still in the experimental phase, holds transformative potential by directly addressing the autoimmune issues that cause Type 1 diabetes.

In addition, treatments using pluripotent stem cells and advanced cell therapy are being explored to regenerate damaged pancreatic cells, thereby offering a more permanent solution for Type 1 diabetes patients.
Emerging Solutions for Type 2 Diabetes: GLP-1-Based Medications
While Type 2 diabetes is largely manageable through lifestyle changes and medication, the growing prevalence of the condition has fueled the development of new drugs. GLP-1 receptor agonists have emerged as leading treatments for Type 2 diabetes, aiding in both blood glucose management and weight loss. Medications like Ozempic and Mounjaro have become popular for their ability to mimic GLP-1, a hormone that promotes insulin production and appetite regulation.
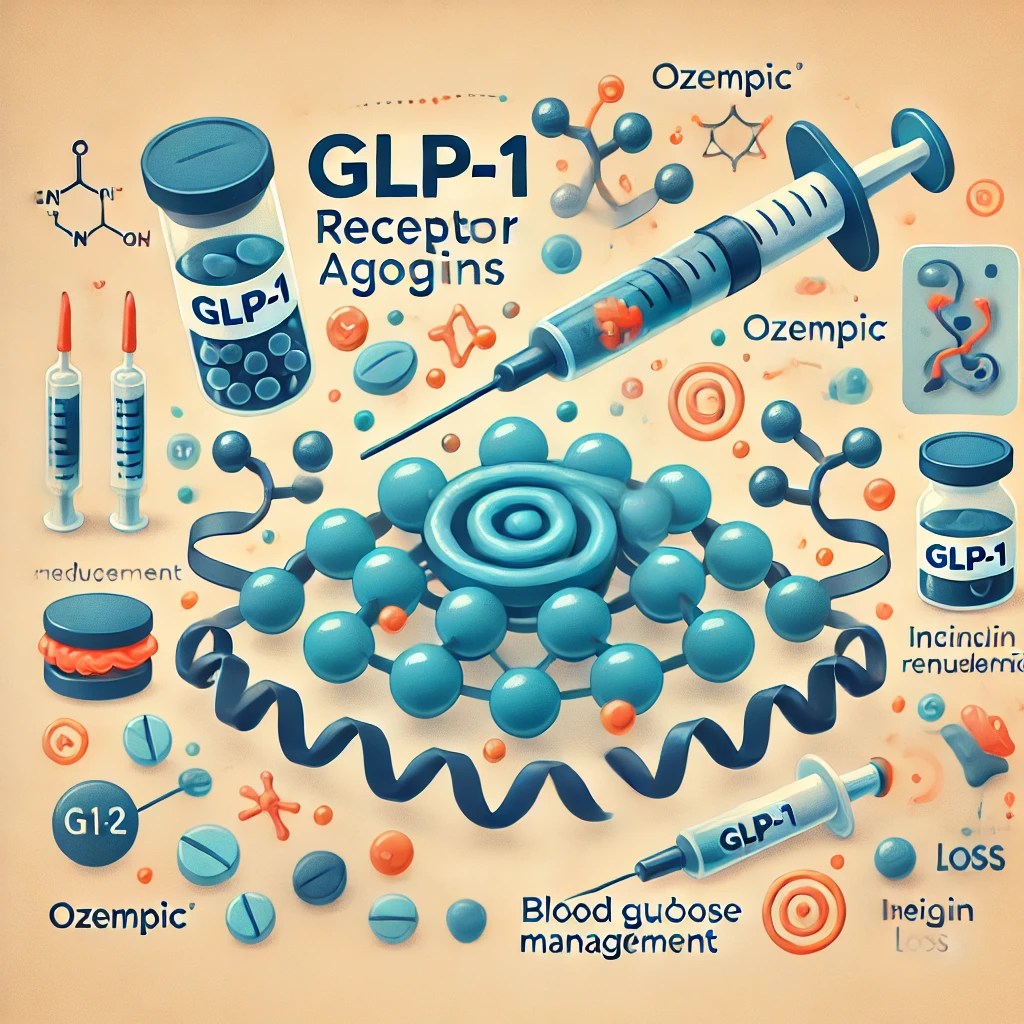
Illustration that expresses the treatment of type 2 diabetes through GLP-1 receptor agonists visually shows the function of blood sugar management and appetite control, making it easy to convey relevant information.
Research into GLP-1-based treatments is also showing promise for younger populations, who are experiencing rising Type 2 diabetes rates. With these drugs showing remarkable results, the future of Type 2 diabetes management looks promising. Ongoing clinical trials continue to test these medications, potentially expanding options for millions of patients worldwide.
Comparing Pancreatic Cell Transplantation, Gene Therapy, and GLP-1 Medications
Each of these innovative approaches offers unique benefits depending on the type of diabetes:
- Pancreatic Cell Transplantation: Offers a direct solution to insulin deficiency for both Type 1 and advanced Type 2 diabetes patients. The goal is to reduce or eliminate the need for insulin injections.
- Gene Therapy (CRISPR): Primarily targeted at Type 1 diabetes, it addresses autoimmune responses, potentially providing a lasting solution for insulin production.
- GLP-1 Medications: Primarily designed for Type 2 diabetes, these drugs enhance insulin production and support weight management, improving overall health for individuals with insulin resistance.
Understanding Diabetes Types and Treatment Options
In simple terms:
- Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune condition that damages insulin-producing pancreatic cells, requiring insulin injections for management.
- Type 2 Diabetes develops from insulin resistance due to factors like genetics, obesity, and diet, affecting approximately 90% of the diabetic population.
Infographic: Diabetes Treatment Innovations
To enhance understanding, our infographic illustrates the key differences between these treatment methods and provides a visual overview of how pluripotent stem cells and gene therapy work to combat diabetes. By comparing each treatment’s benefits, you can get a clearer picture of how these advancements target different aspects of diabetes.

Why Advancements in Diabetes Treatment Matter
Given that 537 million adults were estimated to be living with diabetes in 2021—a number projected to rise to 643 million by 2030—the demand for innovative treatments is urgent. Modern approaches like pancreatic cell transplantation, gene therapy, and GLP-1 receptor agonists represent hope for improving the quality of life and health outcomes for these individuals.
To make a difference, consider supporting diabetes research initiatives or joining an awareness campaign. With each small step forward, we bring the global medical community closer to effective, sustainable diabetes solutions.
Are you interested in learning more about diabetes research? Share your thoughts in the comments below, and let’s discuss the future of diabetes treatment together!

Leave a comment