Blockchain technology has evolved far beyond its cryptocurrency origins, emerging as a major technological force with applications across finance, healthcare, supply chains, and more. This article breaks down the basics of blockchain for those unfamiliar with the technology, explores key concepts in detail, and provides real-world examples to illustrate its transformative potential. With a blend of clear explanations and practical examples, let’s explore the world of blockchain.

1. What is Blockchain, and How Does It Work?
At its most fundamental level, blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that stores data in blocks chained together in chronological order. Unlike traditional databases, blockchain is unique because it doesn’t rely on a central authority. Instead, it operates across a network of computers, making it highly secure and nearly tamper-proof.
How Blockchain Works in Simple Terms
Imagine a shared Google Document: each time you update it, others with access can see the changes. Blockchain functions similarly, with each new “update” verified by all network participants (known as “nodes”) before it is added to the ledger as a “block.” This distributed verification process means no single entity controls the data, enhancing security and transparency.
- Real-World Example: In the financial sector, this decentralized verification is invaluable for transactions, where it ensures data accuracy without needing a trusted third party.
Common Misconceptions:
- It’s Not Just for Cryptocurrency: While blockchain is the backbone of cryptocurrencies, it has applications in numerous industries.
- Blockchain and Bitcoin Are Different: Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency that uses blockchain, but blockchain is simply a technology that can support countless other uses.

2. The Key Advantages of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has several advantages that are reshaping industries around the world. Here are some of its most impactful benefits:
Transparency and Security
Each blockchain participant has access to the transaction history, creating transparency. Moreover, because data is verified across a network, it’s incredibly difficult for a single party to alter records—making it highly secure.
- Example in Supply Chains: Walmart leverages blockchain to track food sources, improving transparency and reducing foodborne illness outbreaks by quickly identifying contaminated batches.
Decentralization and Direct Transactions
Blockchain’s decentralized design allows for peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. This is especially useful for industries reliant on secure, trust-based transactions, such as finance and real estate.
- Example in Finance: Decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, like Compound and Uniswap, enable users to lend, borrow, or trade without banks, reducing costs and increasing accessibility.

Immutability and Data Integrity
Once data is added to a blockchain, it cannot be modified, enhancing data integrity. This immutability is particularly valuable in fields where record-keeping accuracy is paramount, such as healthcare.
- Example in Healthcare: Projects like MedRec use blockchain to protect patient records, giving authorized personnel secure access while preventing unauthorized changes.
3. Blockchain’s Expanding Applications in Various Industries
Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain’s adaptability makes it useful across multiple fields. Here are some ways it is changing industries today:
Finance and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Blockchain has created a new world of decentralized finance (DeFi), allowing people to access financial services without banks. DeFi offers lending, borrowing, and trading services through smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements coded directly onto the blockchain.
- Example: Platforms like Aave allow users to earn interest by lending their assets without a bank, reducing transaction fees and processing time.
Healthcare
Blockchain can securely store sensitive medical records, giving patients more control over their data. By using blockchain, healthcare providers ensure that data is not altered, keeping patient history accurate.
- Example: Chronicled, a blockchain project, tracks prescription drugs across the supply chain to prevent counterfeit medications and enhance patient safety.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain is ideal for supply chain transparency. Each step of a product’s journey, from manufacturing to delivery, can be tracked, making it easier to verify the authenticity and condition of goods.
- Example: IBM’s TradeLens platform monitors global shipping data, enabling companies to trace each container’s journey and prevent fraud.
Voting and Governance
Blockchain’s transparency and security make it a promising solution for voting systems, offering a transparent and tamper-proof record of each vote.
- Example: In the 2018 midterm elections, West Virginia ran a pilot blockchain voting system for military personnel stationed abroad, providing a secure alternative for absentee ballots.
Energy Sector
Blockchain is enabling new energy-sharing platforms that let users trade excess solar energy with neighbors, reducing reliance on traditional power grids and supporting renewable energy initiatives.
- Example: Power Ledger, a blockchain-based company, allows users to sell surplus solar power to neighbors, promoting renewable energy and decentralizing the energy grid.
4. Emerging Trends in Blockchain
Blockchain technology is continually evolving, with several emerging trends promising to make it even more impactful.
Web 3.0 and Decentralized Internet
Blockchain is key to Web 3.0, a decentralized internet where users control their data. Unlike today’s internet, where corporations own vast amounts of user data, Web 3.0 seeks to return control to individuals.
- Example: Decentralized applications (DApps) on Ethereum enable users to interact and transact without giving up data control.
Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Smart contracts automate transactions based on preset conditions. Ethereum and Solana, for instance, support decentralized applications (DApps) for various uses, from gaming to social media.
- Example: Axie Infinity, a blockchain game, allows players to earn cryptocurrency by trading and breeding virtual creatures, illustrating blockchain’s potential in the gaming industry.
Layer-2 Scaling Solutions
Blockchain’s scalability remains a challenge. Layer-2 solutions, such as sidechains and rollups, help increase blockchain’s transaction capacity without compromising security.

- Example: Polygon is a popular layer-2 scaling solution that enables faster and cheaper transactions on the Ethereum network.
5. Challenges and Considerations
While blockchain has substantial benefits, it also faces several challenges:
Scalability Issues
As blockchains grow, so does the amount of data, slowing down transaction speeds. Layer-2 solutions and sharding are being developed to address this.
Regulatory Concerns
The decentralized nature of blockchain can clash with traditional regulations, making it challenging for governments to enforce compliance. Clear regulatory frameworks are needed to ensure blockchain’s safe expansion.
Energy Consumption
Some blockchains, like Bitcoin, consume large amounts of energy due to their proof-of-work consensus mechanism. Ethereum’s shift to proof-of-stake with Ethereum 2.0 aims to make blockchain more sustainable.
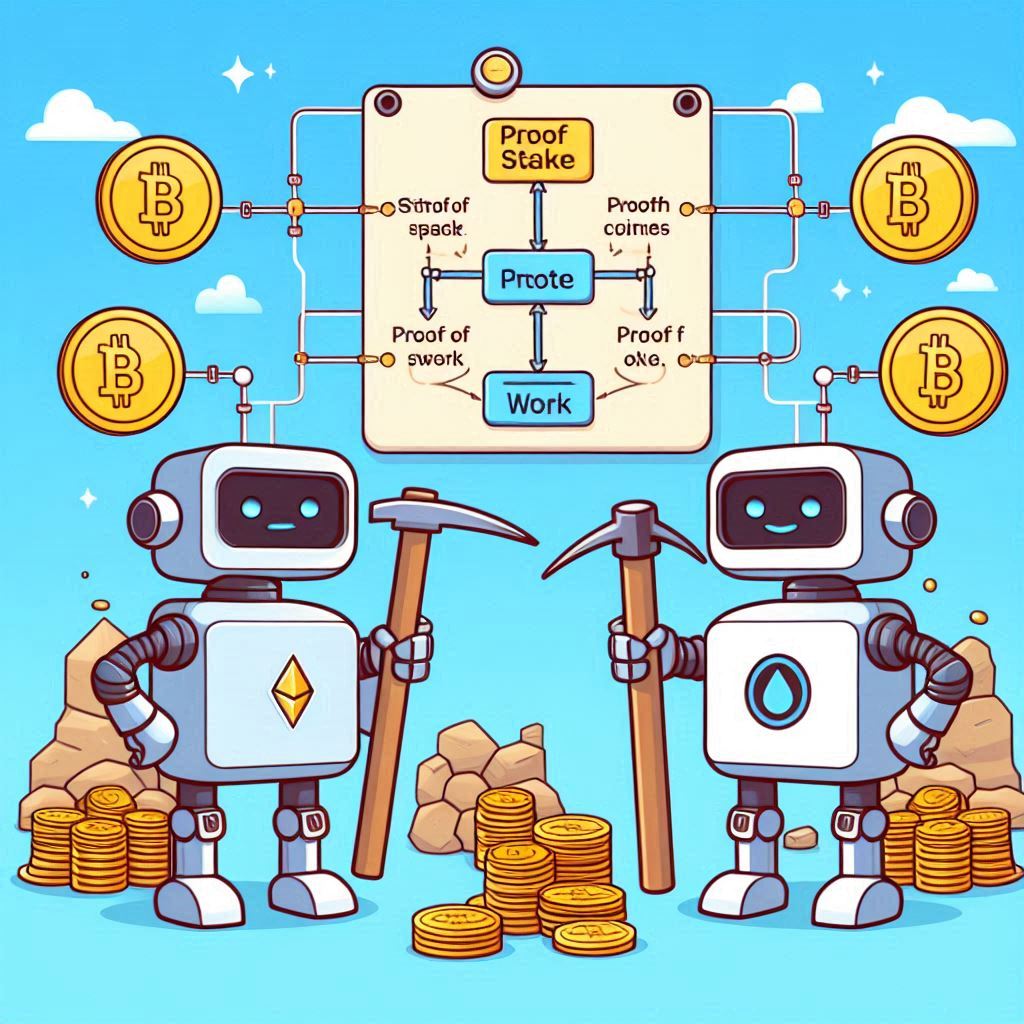
On the other hand, efforts to solve the problem of energy consumption in blockchain have really important implications. Understanding the difference between Proof of Work and Proof of Stake is essential in discussing the sustainability of blockchain technology.
6. How to Start Learning About Blockchain
If you’re intrigued by blockchain’s potential, here are some ways to begin your exploration:
- Learn Basic Concepts: Start with beginner courses on Coursera or edX to understand decentralization, cryptography, and smart contracts.
- Try a Wallet and Cryptocurrency Exchange: Set up a digital wallet and use exchanges like Coinbase or Binance to buy a small amount of cryptocurrency and get hands-on experience.
- Read Blockchain Whitepapers: Start with the Bitcoin Whitepaper by Satoshi Nakamoto to understand blockchain’s original vision and explore whitepapers from newer projects.
- Engage with Blockchain Communities: Join forums, attend webinars, and participate in blockchain meetups or hackathons to stay informed and connect with experts.

Conclusion: Blockchain’s Transformative Power
Blockchain’s decentralized, transparent, and secure nature makes it a technology with immense potential. While it faces challenges like scalability and regulatory concerns, the progress seen in applications across finance, healthcare, and supply chains suggests a promising future. As more people engage with blockchain technology, we are likely to see even more innovative uses that continue to reshape industries and empower individuals.
What aspects of blockchain interest you the most? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below, and let’s discuss how blockchain could shape the future!
Leave a comment