With AI becoming increasingly integrated into our daily lives, one pressing question keeps surfacing: Will AI replace all jobs? It’s a legitimate concern, especially with AI rapidly transforming industries like healthcare, finance, and retail. According to a study by the World Economic Forum, by 2025, AI could displace 85 million jobs globally but simultaneously create 97 million new roles. The reality is that while AI may automate some tasks, it will also open doors to new job opportunities, particularly in areas requiring creativity, emotional intelligence, and complex decision-making.
In this article, we’ll explore how AI will reshape the job market, provide real-world examples, discuss the types of jobs most vulnerable to automation, and offer strategies for adapting to this evolving landscape.
AI and Job Automation: What Will Change?
AI excels at automating repetitive, data-driven, and rule-based tasks. From processing vast amounts of information to performing predictable operations, AI can handle these tasks more efficiently than humans. According to McKinsey & Company, around 45% of current job tasks could be automated using existing technology, impacting roles in sectors like manufacturing, data entry, and customer service.
However, it’s crucial to understand that automation doesn’t always mean complete job elimination. AI is more likely to take over specific tasks within jobs, allowing workers to focus on higher-value activities such as strategic planning, innovation, or personal interactions.
Example:
In healthcare, AI systems are already being used to analyze medical images, quickly diagnosing diseases like cancer. This speeds up the diagnostic process, allowing doctors to spend more time on treatment plans and patient care, rather than spending hours manually reviewing images.
Key Point: AI will automate repetitive tasks, but humans will still be needed for roles that require creativity, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence.
SEO Keywords: AI job automation, AI in the workforce, future of work with AI
Jobs Most Likely to Be Replaced by AI
AI’s ability to perform routine tasks faster and more efficiently makes certain jobs highly susceptible to automation. These include roles that involve predictable, rule-based activities, such as:
- Manufacturing and assembly line workers: Automation has been transforming this sector for years, and AI-driven robots are capable of handling tasks like material handling and product assembly.
- Data entry clerks: AI systems can now process and organize data with better accuracy and at a much faster pace.
- Telemarketers: Automated systems are taking over outbound calls, providing scripted information, and even processing sales.
- Basic customer service roles: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle common customer inquiries, schedule appointments, or troubleshoot simple issues.
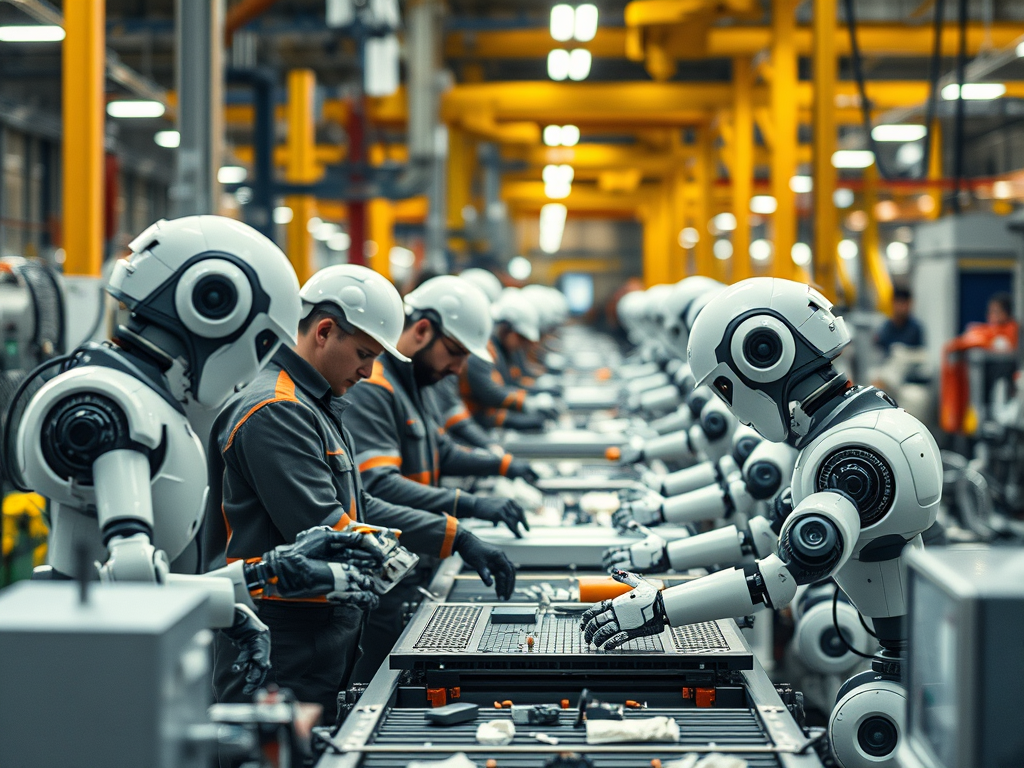

Key Point: Jobs that are routine, repetitive, and primarily involve data processing or manual tasks are most at risk of being replaced by AI.
*** jobs AI will replace, high-risk jobs for automation, automation and job loss
AI-Proof Jobs: The Value of Creativity, Emotional Intelligence, and Complex Decision-Making
While AI will impact many jobs, it’s unlikely to replace roles that require human creativity, emotional depth, or complex decision-making anytime soon. These types of jobs rely on distinctly human skills—skills that AI struggles to replicate.
1. Creativity:
Creative roles, such as those in marketing, design, art, and content creation, require human imagination and emotional intelligence. AI can assist with certain creative tasks—like generating basic content or offering data-driven insights—but the ability to produce deeply resonant work remains uniquely human.
Example:
AI can generate music or artwork based on patterns and data, but it lacks the human experience and originality needed to create truly meaningful or culturally relevant pieces. While AI tools can assist marketers in analyzing trends, it’s still up to human creativity to craft emotionally compelling campaigns that connect with consumers on a deeper level.

2. Emotional Intelligence:
AI may be good at analyzing data, but it’s still far from replicating genuine empathy or emotional understanding. Jobs in healthcare, education, and counseling, for instance, require deep emotional intelligence—something AI cannot provide. These fields depend on building trust and maintaining human connections, which machines aren’t equipped to handle.
Example:
A patient may rely on AI to help diagnose a disease, but it’s the human doctor who offers emotional support, explains complex diagnoses, and guides patients through their treatment journey. This emotional connection is irreplaceable in healthcare and other caregiving professions.
3. Complex Decision-Making:
When it comes to making high-stakes decisions that involve critical thinking, ethics, or long-term strategy, AI falls short. While it can offer data-driven insights, the ability to navigate uncertain or ambiguous situations, consider ethical implications, and make decisions that balance competing interests is inherently human.
Example:
A business executive must not only analyze market trends but also consider company culture, stakeholder interests, and ethical ramifications when making strategic decisions. AI may provide valuable data, but it lacks the human judgment required for these complex scenarios.

Key Point: Jobs requiring creativity, emotional intelligence, and complex decision-making are less likely to be automated and will grow in importance as AI continues to evolve.
*** AI-proof jobs, jobs AI can’t replace, future of human work with AI
Real-World Case Studies of AI in the Workforce
Case Study 1: Amazon Warehouses
Amazon has integrated AI and robotics into its warehouses to streamline the packing and shipping process. Robots now handle product transportation and organization, speeding up delivery times. However, these innovations haven’t eliminated human workers. Instead, workers are now focusing on overseeing the robots, managing quality control, and handling complex logistics.
Case Study 2: AI in Legal Research
Law firms are using AI to automate legal research, reviewing contracts and legal documents far faster than human lawyers can. While this automation reduces the need for entry-level legal researchers, it also allows lawyers to focus on strategy, negotiation, and client interaction—tasks where human insight and creativity are crucial.
Key Point: Real-world examples show that AI is transforming industries, but human oversight and strategic input remain vital.
*** AI case studies, AI in the workforce, real-world AI applications
New Jobs Created by AI: Opportunities in the Tech-Driven Economy
While AI may displace certain jobs, it will also create new roles—especially in areas like AI system design, data analysis, AI ethics, and human-machine collaboration. The World Economic Forum reports that 97 million new jobs could emerge by 2025, with many of these roles centered around managing and improving AI technologies.
Emerging Roles in the AI Economy:
- AI Trainers: Professionals who teach AI systems to recognize patterns, improve their decision-making, and avoid biases.
- Data Scientists: As businesses increasingly depend on AI for insights, data scientists will play a crucial role in analyzing and interpreting large datasets.
- AI Ethics Specialists: With AI’s expanding influence, there’s a growing need for experts who can ensure these technologies are used ethically and transparently.
- Human-AI Interaction Designers: These designers focus on improving the way people interact with AI systems, creating intuitive interfaces and seamless workflows.

Key Point: AI will create new jobs, particularly in fields related to data science, AI ethics, and human-AI collaboration.
*** new jobs created by AI, AI-driven careers, emerging jobs in AI
Adapting to the AI Revolution: Solutions for Workers Displaced by AI
As AI continues to automate certain tasks, workers in affected industries may face job displacement. However, there are solutions that can help displaced workers transition into new roles or even entire new fields. Governments, companies, and educational institutions will play a crucial role in this transition, providing upskilling and reskilling programs.
Strategies for Workers:
- Upskilling and Reskilling:
Workers can transition to new roles by learning new skills, especially in tech-related fields. Many online platforms, such as Coursera and Udemy, offer affordable courses in areas like coding, data analysis, and AI. - Focusing on Soft Skills:
As automation takes over technical tasks, soft skills—like communication, leadership, and emotional intelligence—will become increasingly important. Workers who focus on developing these skills will be better positioned for future job opportunities. - Exploring New Career Paths:
For workers displaced by AI, exploring industries that are less likely to be automated—such as healthcare, education, and the arts—can offer a fresh start and new opportunities.

Key Point: Workers displaced by AI can transition into new roles by learning new skills, developing soft skills, and exploring industries that are less susceptible to automation.
*** upskilling for AI, solutions for displaced workers, reskilling for AI jobs
Conclusion: Human-AI Collaboration is the Future of Work
AI is not going to replace all jobs, but it will change the nature of work. While some routine tasks will be automated, new opportunities will arise for jobs that require human creativity, emotional intelligence, and complex decision-making. The future of work will be one of human-AI collaboration, where AI handles time-consuming tasks, and humans focus on innovation, strategy, and empathy-driven roles.
To succeed in the AI-driven future, workers must be proactive in developing skills that AI cannot easily replicate. By embracing lifelong learning, cultivating emotional intelligence, and staying adaptable, you’ll not only safeguard your career but thrive in the evolving workforce.
Call-to-Action:
Prepare for the future of work by developing essential skills. Consider enrolling in online courses through platforms like Coursera, Udemy, or LinkedIn Learning to boost your knowledge in areas like AI, data science, creativity, and emotional intelligence. By taking steps now to upskill, you can position yourself for success in the age of AI and thrive in a rapidly changing job market.

Leave a comment