Did you know that one-third of adults don’t get the recommended amount of sleep each night? According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), insufficient sleep has been linked to a variety of health problems, including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and even early mortality. But sleep is about more than just avoiding health risks—it’s a cornerstone of how our bodies and minds function optimally. From strengthening your immune system to enhancing mental clarity and supporting physical recovery, sleep plays a far more significant role in our health than many realize.
In this article, we’ll explore the vital impact of quality sleep on your immune system, mental health, and physical well-being. We’ll also provide actionable tips to improve your sleep and enhance overall health.
The Role of Sleep in Boosting Immune Function
Sleep and your immune system are closely linked. While you sleep, your body produces proteins known as cytokines, which play a key role in fighting infection and inflammation. In fact, research published in Sleep shows that people who regularly sleep fewer than seven hours are three times more likely to catch a cold than those who get eight or more hours of sleep per night.
Why does this happen? When you’re sleep-deprived, your body produces fewer cytokines and other infection-fighting antibodies, leaving your immune system vulnerable. Adequate sleep ensures that your body is equipped to ward off illnesses, ranging from the common cold to more serious infections.
Here’s the illustration depicting the impact of sleep on the immune system, showing a well-rested person with a robust immune system contrasted against a sleep-deprived person with a vulnerable immune system. This visual can effectively complement your discussion on how sleep affects health.
Key Point: A well-rested immune system is your first line of defense against illness. Prioritizing sleep helps your body maintain the resources needed to fight off infections.
SEO Keywords: sleep and immune function, how sleep supports immune health, sleep and infection prevention
Sleep and Mental Health: The Cognitive and Emotional Connection
Ever notice how a sleepless night can leave you feeling foggy, irritable, or anxious the next day? Sleep is vital to cognitive function and emotional well-being. During sleep, the brain processes and consolidates memories, clears out toxins, and balances mood-regulating neurotransmitters.
Chronic sleep deprivation, on the other hand, has been linked to an increased risk of mental health issues such as depression and anxiety. Studies show that people who consistently get enough sleep experience better memory recall, improved decision-making, and greater emotional resilience.
Example:
I once tried to juggle long workdays with late-night Netflix binges, consistently sleeping less than six hours per night. Over time, I noticed not only a decline in my focus at work but also increased irritability. However, when I committed to getting at least seven hours of sleep, my mood improved, I felt less stressed, and my cognitive performance skyrocketed.
Broader Perspective:
Beyond personal experience, people from diverse backgrounds—students, parents, professionals, and even retirees—report similar cognitive and emotional benefits from regular, quality sleep. Sleep is a universal need that cuts across all demographics, making it essential for everyone.

Key Point: Sleep is crucial for maintaining optimal brain function and emotional health, enhancing memory, mood regulation, and overall cognitive abilities.
SEO Keywords: sleep and mental health, cognitive benefits of sleep, sleep for emotional well-being
The Power of Sleep for Physical Recovery and Health
When we think about physical health, we often focus on diet and exercise. But sleep is just as critical—if not more so—when it comes to maintaining physical well-being. During sleep, the body works to repair muscles, regenerate tissues, and produce essential hormones like growth hormone, which helps the body recover from the day’s exertions.
Sleep also plays a vital role in metabolism and weight management. Sleep-deprived individuals are more likely to experience an imbalance in hunger-regulating hormones, leading to overeating and weight gain. Lack of sleep is also linked to a higher risk of developing conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and hypertension.
Example from Athletes:
Many elite athletes, including LeBron James and Serena Williams, have emphasized that sleep is a key part of their training regimen. They often aim for 8-10 hours of sleep per night to help their bodies fully recover after intense physical activity. Their focus on sleep as part of their performance strategy highlights its role in optimizing physical recovery and endurance.

Key Point: Whether you’re an athlete or simply looking to stay healthy, sleep is essential for muscle recovery, metabolism regulation, and overall physical well-being.
SEO Keywords: sleep for physical health, sleep and muscle recovery, sleep and metabolism
Sleep and Emotional Health: Managing Stress and Mood
It’s no surprise that poor sleep can leave you feeling more irritable, but what’s less known is how deeply sleep impacts our ability to handle stress and regulate emotions. When you’re well-rested, your brain has a better capacity to process emotions and respond calmly to stressors. In contrast, lack of sleep can lead to mood swings, anxiety, and heightened emotional reactivity.
Studies have shown that people who don’t get enough sleep are more likely to focus on negative experiences and less able to manage stress. Adequate sleep helps balance your emotional state, making you more resilient in the face of life’s daily challenges.
Quote from Expert:
Dr. Matthew Walker, author of Why We Sleep, notes, “Sleep deprivation is emotionally destabilizing. When you’re sleep-deprived, you are more likely to have stronger negative reactions to events, and it’s much harder to maintain emotional control.”
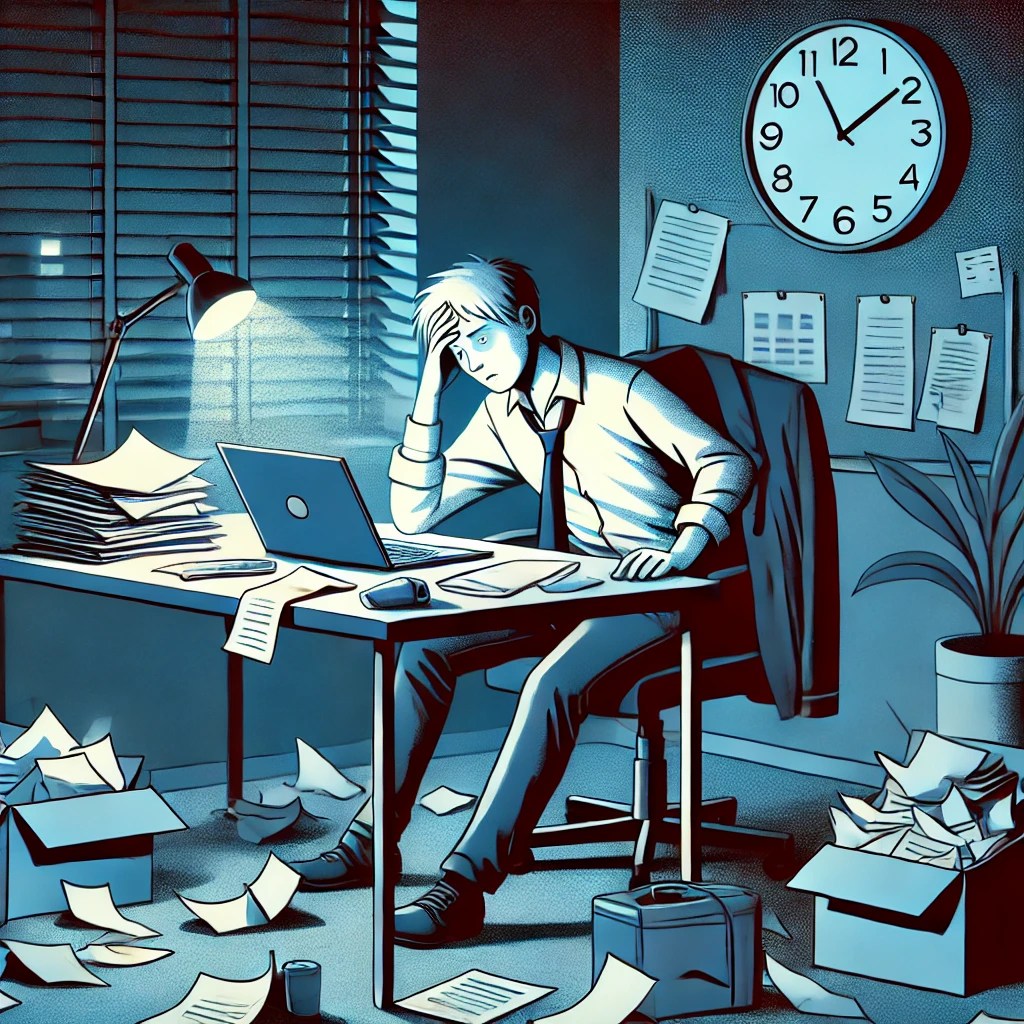

Here’s the illustration related to the effects of sleep deprivation, depicting a person overwhelmed and exhausted at their work desk. This visual conveys the emotional challenges associated with lack of sleep as described by Dr. Matthew Walker.
Key Point: Sleep is essential for emotional balance, helping you manage stress and maintain a positive outlook on life.
SEO Keywords: sleep and emotional health, sleep for stress management, how sleep affects mood
Sleep and Weight: How Lack of Sleep Contributes to Weight Gain
If you’ve ever noticed yourself craving junk food after a poor night’s sleep, you’re not alone. Sleep deprivation disrupts the balance of hunger hormones ghrelin (which stimulates appetite) and leptin (which signals fullness). As a result, you may find yourself feeling hungrier and more likely to overeat, especially high-calorie, sugary foods.
Beyond cravings, sleep deprivation can also negatively affect insulin sensitivity, which is linked to increased risk for type 2 diabetes. Poor sleep leads to disruptions in how your body processes glucose, making it harder to maintain a healthy weight and manage blood sugar levels.

Key Point: Getting enough sleep is crucial for weight management. Sleep deprivation not only increases hunger but also affects how your body processes and stores food.
SEO Keywords: sleep and weight gain, sleep and appetite control, how sleep affects metabolism
Actionable Tips to Improve Your Sleep Quality
Improving your sleep quality doesn’t require drastic lifestyle changes—small adjustments can make a big difference. Here’s how to start sleeping better:
- Set a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day helps regulate your body’s internal clock. Consistency trains your body to expect sleep at a certain time, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up feeling refreshed.
- Create a Relaxing Pre-Sleep Routine: Activities like reading, deep breathing, or taking a warm bath can signal your body that it’s time to wind down. This helps transition your mind from the day’s stress to a more relaxed state.
- Limit Screen Time Before Bed: Blue light from phones, tablets, and computers interferes with the production of melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep. Try reducing screen exposure an hour before bedtime to help your body prepare for rest.
- Optimize Your Sleep Environment: Make your bedroom a sleep-friendly space by ensuring it’s cool, dark, and quiet. Consider blackout curtains and a comfortable mattress to improve your sleep environment.
- Watch What You Eat and Drink: Avoid caffeine, heavy meals, and alcohol close to bedtime, as these can disrupt your ability to fall and stay asleep.

This image depicts a serene bedroom setting designed to enhance sleep, with elements like reading before bed and limited screen time highlighted.
For additional guidance on improving sleep, apps like Sleep Cycle and Calm provide personalized insights and relaxation techniques to enhance your sleep routine.
Key Point: Consistency, environment, and mindful pre-sleep habits are key factors in improving the quality of your sleep.
SEO Keywords: tips for better sleep, improve sleep quality, sleep hygiene tips
Conclusion: Sleep is the Foundation of Optimal Health
In the quest for better health, sleep is often the unsung hero. Whether it’s supporting your immune system, improving mental clarity, aiding in physical recovery, or regulating your emotions, sleep plays a vital role in every aspect of your well-being. If you’re looking to boost your health, start by prioritizing your sleep. Small changes in your sleep habits can lead to big improvements in how you feel, think, and perform.
Summary of Key Points:
- Quality sleep strengthens the immune system, improving the body’s ability to fight off infections.
- Adequate sleep boosts cognitive function, enhancing memory, decision-making, and emotional regulation.
- Sleep aids in muscle recovery, metabolism regulation, and overall physical health.
- Emotional balance and stress management are directly linked to good sleep habits.
- Poor sleep contributes to weight gain by disrupting hunger hormones and insulin sensitivity.
Call-to-Action:
Ready to take control of your sleep? Start by implementing just one of the tips mentioned above, whether it’s limiting screen time before bed or optimizing your sleep environment. With better sleep, you’ll notice improvements not just in your energy levels but across all aspects of your health. And don’t forget to explore apps like Sleep Cycle or Calm to track your progress and optimize your rest.

Leave a comment